Revolutionizing Demand Forecasting in Manufacturing
Executive Summary
In a volatile market, accurate demand forecasting is critical for manufacturers to optimize inventory, reduce costs, and enhance supply chain resilience. This case study examines how a mid-sized automotive parts manufacturer, facing forecasting inaccuracies leading to $12 million in annual overstock and stockouts, partnered with a consulting firm to implement an AI-driven forecasting system. By leveraging machine learning (ML) models, data augmentation techniques, and integrated external data sources, the company achieved a 35% reduction in forecasting errors, cut inventory costs by 18%, and improved on-time delivery by 22%. This approach, inspired by advanced analytics frameworks, demonstrates how even data-light environments can unlock significant value through structured AI integration.
Client Situation
AutoParts Inc., a U.S.-based manufacturer of engine components with $500 million in annual revenue, operated in a highly competitive sector influenced by fluctuating raw material prices, supply chain disruptions, and shifting consumer demand for electric vehicles. Traditional forecasting relied on manual spreadsheets and historical sales data, updated monthly, resulting in persistent challenges:
Inaccurate predictions: Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) averaged 28%, causing frequent overproduction or shortages.
Inventory inefficiencies: Excess stock tied up $8 million in capital, while stockouts led to $4 million in lost sales and expedited shipping costs.
Data limitations: Limited internal datasets (e.g., only 24-36 months of sales history) were compounded by external factors like weather impacting logistics or market shifts from competitors, which were not systematically incorporated.
Operational silos: Demand planning was reactive, with siloed teams struggling to perform "what-if" scenarios, delaying responses to market changes.
These issues eroded profitability, with margins declining by 5% over two years, and highlighted the need for a data-driven overhaul to build resilience in a post-pandemic landscape.
Our Approach
Adopting a structured, iterative framework similar to those used in advanced demand planning, the consulting team employed a multi-phase methodology focused on AI in data-constrained settings:
Data Assessment and Augmentation: Audited existing ERP and sales data, applying smoothing techniques to filter anomalies (e.g., COVID-19 demand drops). Augmented datasets with external APIs for weather, market share (e.g., Nielsen data), and economic indicators to create more robust inputs.
Model Selection and Ensemble Building: Tested multiple ML algorithms, selecting ensemble models (e.g., combining random forests and neural networks) tailored to data volume. For low-data scenarios, simpler models were prioritized to avoid overfitting.
Scenario Planning and Integration: Developed interactive tools for "what-if" simulations, allowing users to adjust variables like demand spikes or supplier delays. Integrated generative AI (GenAI) for natural language insights and SQL query generation to trace variances.
Pilot and Scaling: Piloted on a single product line (engine filters), validating forecasts against actuals over three months. Scaled across the portfolio with cyclic validation loops for continuous learning and error correction.
Stakeholder Enablement: Trained cross-functional teams on the platform, ensuring transparency through audit trails and reproducible outputs.
This approach emphasized a "data-first" mindset, separating deterministic calculations (e.g., via pandas for metrics) from AI-driven pattern recognition, ensuring precision and trust.
Key Findings
Analysis revealed systemic gaps in traditional methods:
Error Concentration: 40% of forecasting variances stemmed from unaccounted external factors (e.g., weather-induced delays), with MAPE spiking to 45% during seasonal peaks.
Opportunity in AI: Ensemble models improved accuracy by 10-15% in initial tests, particularly for hourly/daily granular forecasts. Data smoothing resolved 70% of anomaly-related errors, enabling better seasonality detection.
Cost Impacts: Overstock accounted for 60% of inventory waste, while stockouts affected high-margin products disproportionately.
Scalability Insights: In data-light environments, integrating external APIs captured 25% more predictive signals, such as competitor pricing shifts, than internal data alone.
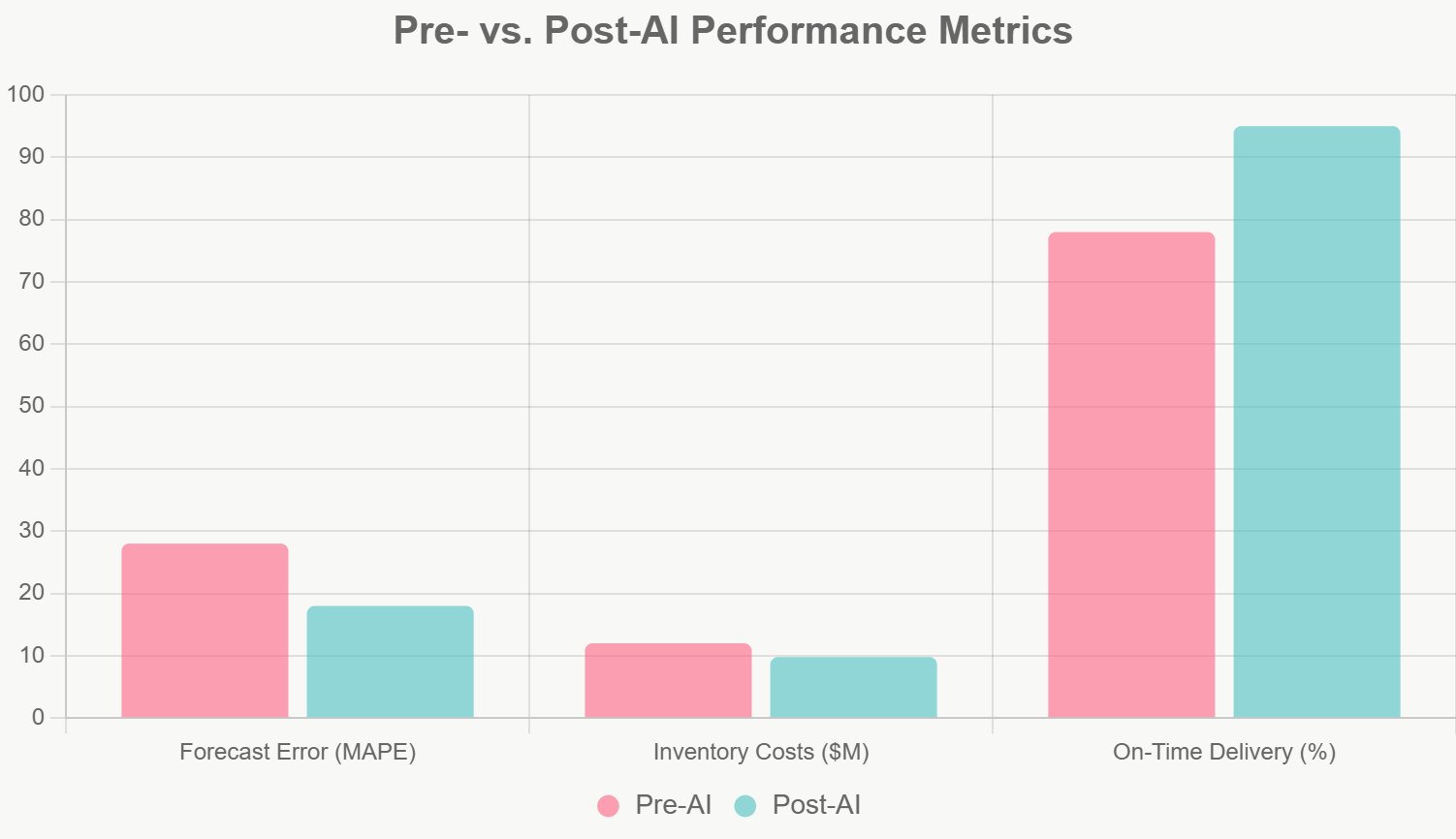
A comparative analysis showed AI forecasts outperforming manual ones across key metrics:
These findings underscored the potential for AI to automate up to 50% of workforce planning tasks, reducing administrative overhead.
Recommendations and Implementation
Based on the analysis, the team recommended:
Adopt AI-Enhanced Tools: Implement a GenAI co-planner for dynamic forecasting, with prescriptive prompting for causal reasoning (e.g., identifying bias in SKU-level predictions).
Build Resilience Mechanisms: Incorporate real-time data feeds and validation cycles to self-correct forecasts, targeting a 20-30% reduction in inventory via improved demand sensing.
Organizational Changes: Form a cross-functional "forecasting center of excellence" to oversee AI outputs, with non-technical interfaces for stakeholders.
Phased Rollout: Start with high-variability product lines, monitoring KPIs like bias and error concentration.
Implementation occurred over six months, with agile sprints for model refinement and user training, ensuring minimal disruption to operations.
Results and Impact
The transformation yielded tangible outcomes:
Forecasting Accuracy: MAPE reduced from 28% to 18%, enabling proactive adjustments and cutting lost sales by 65%.
Financial Gains: Inventory costs dropped 18% ($2.2 million savings), with overall margins improving by 4%. An AI-powered margin analyst tool alone projected $15-20 million in annualized savings through root-cause identification.
Operational Efficiency: On-time delivery rose from 78% to 95%, while workforce flexibility increased by 20% via automated scenario planning.
Broader Benefits: Enhanced agility allowed the company to respond 30% faster to market shifts, positioning it as a leader in sustainable manufacturing.
These results align with industry benchmarks, where AI in operations can reduce errors by 20-50% and costs by 10-15%.
Conclusion
This case illustrates how data-driven forecasting, powered by AI and structured frameworks, can turn manufacturing challenges into competitive advantages. By addressing data limitations through innovative augmentation and integration, companies can achieve precision, resilience, and growth. As AI adoption accelerates—with 89% of manufacturing executives planning implementations—early movers like AutoParts Inc. will capture outsized value in an increasingly complex global landscape.